Azure Backup and Recovery: 7 Powerful Strategies for Ultimate Data Protection
In today’s cloud-driven world, data is the backbone of every organization. With Azure Backup and Recovery, businesses gain a powerful, reliable, and scalable solution to safeguard critical information against loss, corruption, or cyber threats.
Understanding Azure Backup and Recovery: The Foundation of Cloud Resilience
Azure Backup and Recovery is Microsoft’s comprehensive cloud-based data protection service designed to secure workloads across on-premises, hybrid, and cloud environments. It eliminates the complexity of traditional backup systems by offering automated, centralized, and policy-driven backup solutions.
What Is Azure Backup?
Azure Backup is a managed service that enables organizations to back up data from various sources, including virtual machines, databases, file shares, and on-premises servers. It operates on a pay-as-you-go model, reducing infrastructure costs and administrative overhead.
- Backs up data to highly durable Azure storage
- Supports long-term retention and geo-redundancy
- Integrates seamlessly with Azure Monitor and Azure Security Center
According to Microsoft’s official documentation, Azure Backup ensures 99.9% availability of backup data, making it a trusted choice for enterprises.
What Is Azure Site Recovery?
Azure Site Recovery (ASR) complements Azure Backup by focusing on disaster recovery. It replicates virtual machines and physical servers to Azure, enabling rapid failover during outages. While Azure Backup handles data snapshots, ASR ensures business continuity by maintaining system state and application availability.
- Enables near-zero downtime during disasters
- Supports cross-region replication
- Automates recovery plans for faster restoration
“Azure Site Recovery is not just about backup—it’s about ensuring your business never stops.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
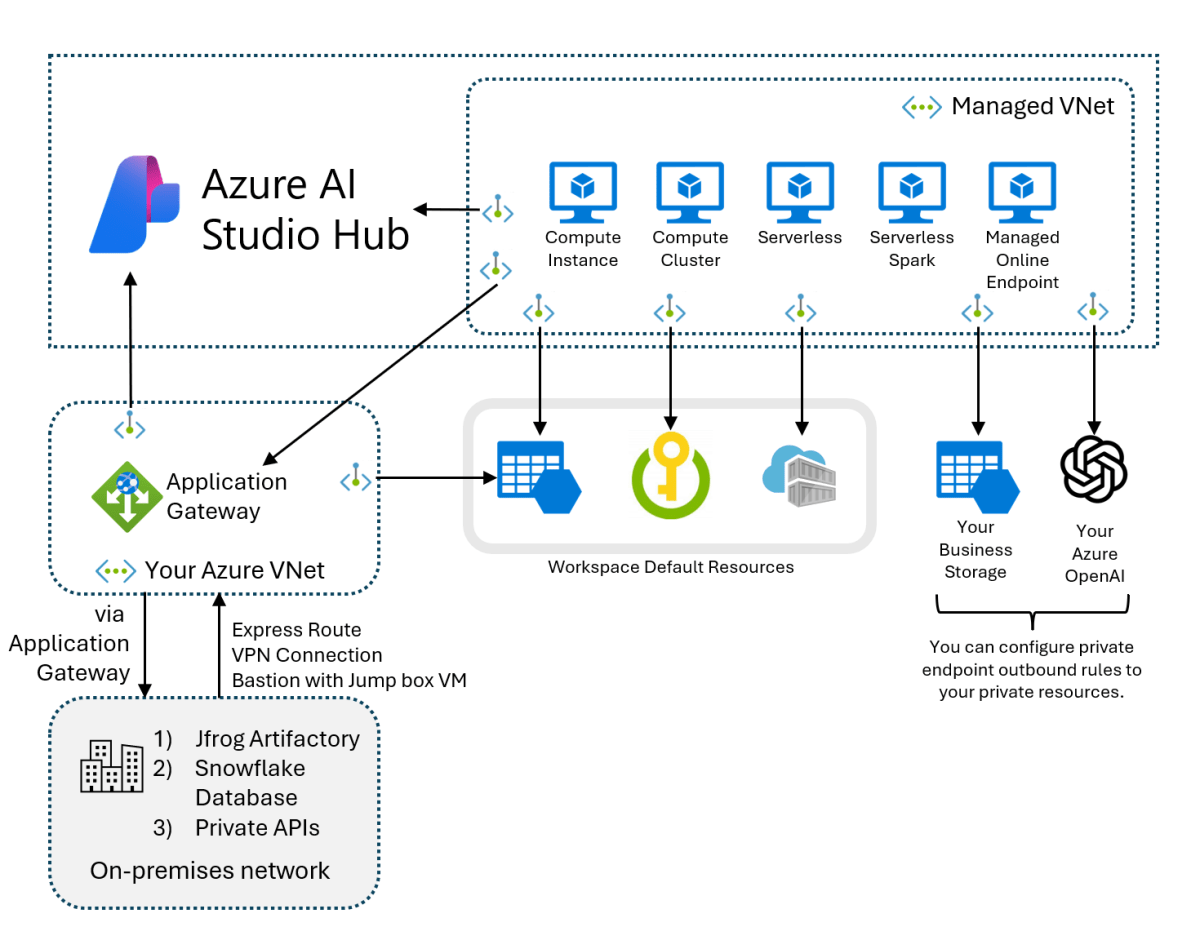
Azure Backup and Recovery: Key Components and Architecture
To fully leverage Azure Backup and Recovery, it’s essential to understand its core components and how they interact within the Azure ecosystem.
Recovery Services Vault
The Recovery Services Vault is the central hub for managing backups in Azure. It stores backup data, policies, and recovery points. Each vault supports multiple workloads, including Azure VMs, on-premises servers, and SQL databases.
- Acts as a secure container for backup data
- Supports encryption at rest using Microsoft-managed or customer-managed keys
- Allows backup retention from days to decades
It’s important to note that while a single vault can manage diverse workloads, best practices recommend separating vaults by region or compliance requirements to enhance security and management.
Backup Policies and Scheduling
Backup policies define when and how often backups occur, as well as retention periods. Azure allows granular control over daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly backup schedules.
- Customizable retention: Keep backups for up to 99 years
- Policy inheritance for consistent backup across VMs
- Integration with Azure Policy for governance
For example, a financial institution might set a policy to back up transaction databases every 4 hours with a 7-year retention period to meet regulatory compliance.
Data Encryption and Security
Security is paramount in Azure Backup and Recovery. All data is encrypted in transit using TLS 1.2+ and at rest using AES-256 encryption.
- Supports Azure Key Vault integration for key management
- Enables private endpoints to block public internet access to the vault
- Complies with ISO 27001, HIPAA, GDPR, and other standards
Organizations handling sensitive data, such as healthcare providers, can leverage these features to meet strict compliance mandates.
Azure Backup and Recovery for Virtual Machines
One of the most common use cases of Azure Backup and Recovery is protecting Azure Virtual Machines (VMs). This section explores how to back up and restore VMs efficiently.
Backing Up Azure VMs
Backing up an Azure VM is straightforward. The process involves enabling backup through the Azure portal, selecting a Recovery Services vault, and applying a backup policy.
- Uses snapshot-based backups for minimal performance impact
- Supports both managed and unmanaged disks
- Allows backup during VM runtime without downtime
Microsoft reports that over 90% of Azure VMs are protected using Azure Backup, highlighting its reliability and ease of use.
Restoring Azure VMs
Restoration can be performed at multiple levels: entire VM, individual disks, or specific files. The restore process is intuitive and can be initiated from the Azure portal.
- Full VM restore: Recreates the VM in the same or different region
- Disk restore: Attaches recovered disks to existing VMs
- File-level recovery: Mounts recovery points as drives to extract files
This flexibility ensures that organizations can respond appropriately to different failure scenarios, from accidental file deletion to complete VM corruption.
Monitoring and Alerts
Azure Monitor and Log Analytics integrate with Azure Backup to provide real-time insights into backup job status, success rates, and potential failures.
- Set up alerts for failed backup jobs
- Generate reports for compliance audits
- Use Azure Dashboards to visualize backup health
Proactive monitoring reduces the risk of undetected backup failures, which could lead to data loss during a real incident.
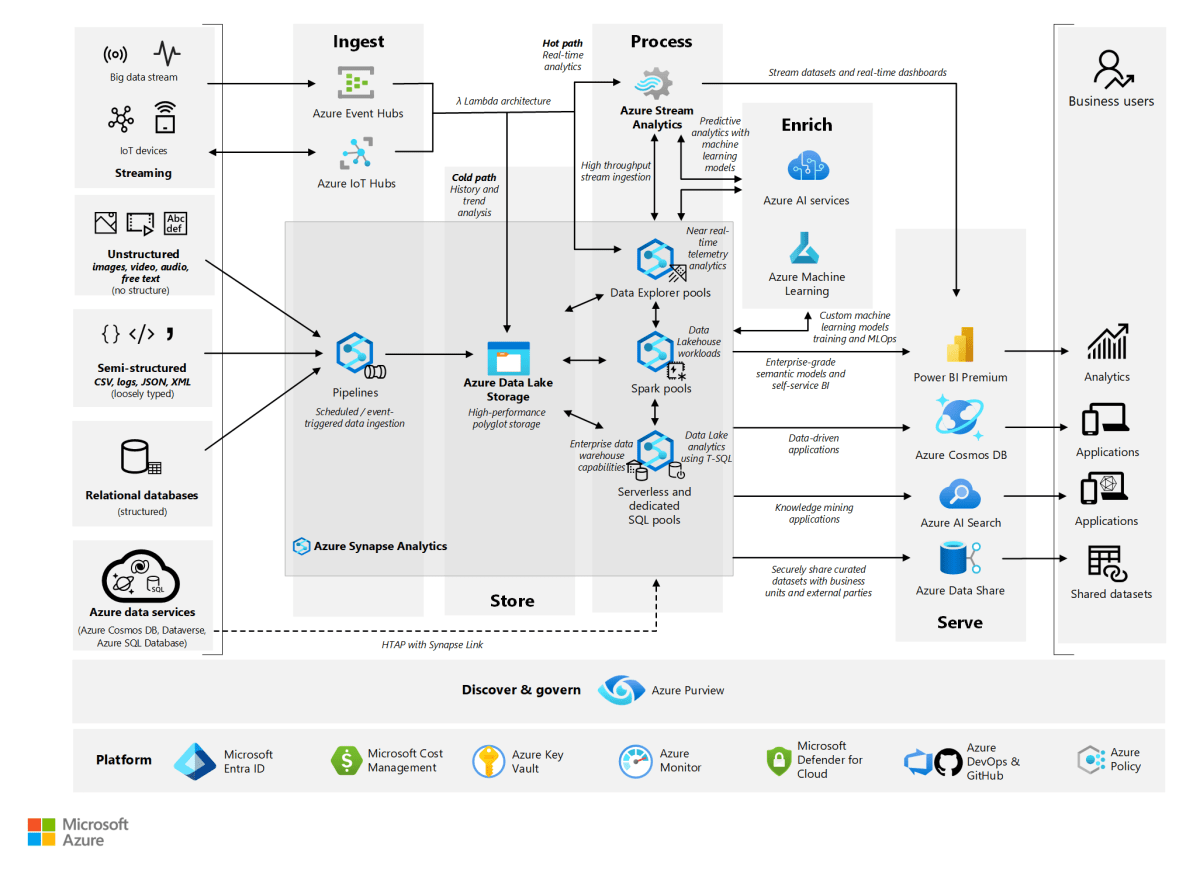
Azure Backup and Recovery for On-Premises Workloads
Not all data resides in the cloud. Azure Backup and Recovery extends protection to on-premises environments through the Microsoft Azure Backup Server (MABS) and Azure Backup Agent.
Using Azure Backup Agent
The Azure Backup Agent (formerly Windows Server Backup) allows direct backup of files and folders from on-premises Windows servers to Azure.
- Lightweight agent with minimal resource usage
- Supports incremental backups to reduce bandwidth consumption
- Enables point-in-time recovery
This is ideal for small to medium businesses that want cloud-based protection without investing in additional hardware.
Azure Backup and Recovery – Azure Backup and Recovery menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Microsoft Azure Backup Server (MABS)
MABS is a more advanced solution for enterprises with complex on-premises environments. It acts as a backup aggregator, supporting applications like SQL Server, SharePoint, and Exchange.
- Integrates with System Center Data Protection Manager (DPM)
- Supports tape integration for hybrid backup strategies
- Provides centralized management for large-scale deployments
MABS is particularly useful for organizations transitioning to the cloud, allowing them to maintain existing backup workflows while leveraging Azure’s scalability.
Backup of Physical Servers
Physical servers can be backed up directly using the Azure Backup Agent or through MABS. This ensures that legacy systems remain protected even if they are not virtualized.
- Supports bare-metal recovery
- Enables disaster recovery for non-cloud-ready infrastructure
- Provides encryption during data transfer
For industries like manufacturing or healthcare, where physical servers still run critical applications, this capability is essential.
Azure Backup and Recovery for Databases
Databases are among the most critical assets in any organization. Azure offers specialized backup solutions for SQL Server, Azure SQL Database, and SAP HANA.
SQL Server Backup to Azure
SQL Server running on Azure VMs or on-premises can be backed up using Azure Backup. The service understands SQL transaction logs and ensures application-consistent backups.
- Automated log truncation after backup
- Supports Always On Availability Groups
- Enables point-in-time restore for granular recovery
This ensures that database integrity is maintained, even during high-transaction periods.
Azure SQL Database Automated Backups
Azure SQL Database includes built-in automated backups with no additional configuration required. These backups are geo-redundant and support long-term retention.
- Daily full backups, differential every 12 hours, transaction logs every 5–10 minutes
- Long-term retention policies (up to 10 years)
- Point-in-time restore across geo-replicated regions
These features make Azure SQL Database one of the most resilient managed database services available.
SAP HANA Backup on Azure
For enterprises running SAP workloads, Azure offers native backup support for SAP HANA through the SAP HANA Backup Service.
- Supports large memory footprints (up to 24 TB)
- Integrates with SAP HANA Studio for management
- Enables fast recovery for mission-critical ERP systems
Given the complexity of SAP environments, this integration simplifies backup operations significantly.
Azure Backup and Recovery: Disaster Recovery with Site Recovery
While Azure Backup focuses on data protection, Azure Site Recovery (ASR) ensures business continuity by enabling disaster recovery for entire systems.
How Azure Site Recovery Works
ASR replicates virtual machines from on-premises Hyper-V or VMware environments to Azure. In the event of a disaster, you can fail over to Azure with minimal downtime.
- Continuous replication with RPO as low as 30 seconds
- Non-disruptive failover testing
- Automated recovery plans with custom scripts
ASR is ideal for organizations that require high availability and compliance with SLAs.
Failover and Failback Procedures
Failover moves workloads to Azure during an outage. Once the primary site is restored, failback migrates operations back.
- Planned failover: For scheduled maintenance
- Unplanned failover: During unexpected outages
- Commit failback only after data synchronization
These procedures ensure minimal disruption and data consistency.
Recovery Plan Customization
Recovery plans allow you to define the order of VM startup, run pre- and post-scripts, and integrate with ITSM tools like ServiceNow.
- Group VMs by application tier (e.g., web, app, database)
- Add PowerShell or bash scripts for configuration
- Integrate with Azure Automation for orchestration
This level of customization ensures that complex applications are restored in the correct sequence.
Best Practices for Azure Backup and Recovery
To maximize the effectiveness of Azure Backup and Recovery, organizations should follow industry best practices.
Implement the 3-2-1 Backup Rule
The 3-2-1 rule recommends keeping three copies of data, on two different media, with one copy offsite. Azure naturally supports this with local and geo-redundant storage options.
- Primary data + two backup copies
- On-premises and cloud storage
- Geo-replicated vaults for offsite protection
This strategy mitigates risks from hardware failure, ransomware, and regional disasters.
Regularly Test Recovery Procedures
Backups are only as good as their ability to be restored. Regular recovery drills ensure that processes work when needed.
Azure Backup and Recovery – Azure Backup and Recovery menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Conduct quarterly restore tests
- Validate data integrity post-recovery
- Document recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO)
Many organizations discover backup issues only during a real crisis—testing prevents this.
Monitor Backup Health and Compliance
Use Azure Monitor, Log Analytics, and Azure Security Center to track backup job success, detect anomalies, and ensure compliance.
- Set up alerts for failed jobs
- Generate compliance reports for auditors
- Use Azure Policy to enforce backup requirements
Proactive monitoring reduces the risk of undetected failures and ensures regulatory adherence.
Cost Optimization in Azure Backup and Recovery
While Azure Backup is cost-effective, improper configuration can lead to unnecessary expenses.
Understanding Pricing Models
Azure Backup uses a consumption-based pricing model based on the amount of protected data and retention period.
- Charges for storage (hot, cool, archive tiers)
- Costs vary by region and redundancy option (LRS, GRS)
- No charges for outbound data during restore
Organizations should review their retention policies to avoid keeping backups longer than necessary.
Leveraging Backup Tiers
Azure introduced backup storage tiers—Standard and Archive—to optimize costs.
- Standard tier: For backups needed within 30 days
- Archive tier: For long-term compliance backups (3+ months)
- Cost savings up to 65% in archive tier
Automated tiering policies can move data from standard to archive based on age.
Right-Sizing Backup Policies
Not all workloads require the same backup frequency. Critical systems may need hourly backups, while others can be backed up weekly.
- Classify data by criticality and RPO
- Avoid over-backing up non-essential data
- Use tags to group resources with similar backup needs
This approach ensures cost efficiency without compromising protection.
What is Azure Backup and Recovery?
Azure Backup and Recovery is a suite of Microsoft Azure services that protect data and applications from loss or corruption. It includes Azure Backup for data snapshots and Azure Site Recovery for disaster recovery and system failover.
How much does Azure Backup cost?
Costs depend on the amount of protected data, retention period, and storage tier. Azure offers a free tier for small workloads and pay-as-you-go pricing for larger deployments. Detailed pricing is available on the Azure pricing page.
Can I back up on-premises servers to Azure?
Yes, you can back up on-premises Windows and Linux servers using the Azure Backup Agent or Microsoft Azure Backup Server (MABS). These tools enable secure, encrypted backup to Azure Recovery Services vaults.
What is the difference between Azure Backup and Azure Site Recovery?
Azure Backup focuses on creating point-in-time copies of data for recovery, while Azure Site Recovery replicates entire virtual machines for disaster recovery and business continuity. They are complementary services.
How do I restore a deleted Azure VM from backup?
You can restore a deleted VM using the Recovery Services vault. Navigate to the vault, select the backup item, choose the recovery point, and restore the VM to its original or a new location. The process preserves disks, configurations, and data.
Azure Backup and Recovery is a cornerstone of modern data protection strategies. Whether you’re safeguarding virtual machines, databases, or on-premises servers, Azure provides a scalable, secure, and cost-effective solution. By leveraging automated policies, encryption, and disaster recovery capabilities, organizations can ensure business continuity in the face of unexpected disruptions. Implementing best practices—such as regular testing, tiered storage, and compliance monitoring—further enhances resilience. As cyber threats and data volumes grow, investing in a robust backup and recovery framework like Azure’s is not just smart—it’s essential.
Azure Backup and Recovery – Azure Backup and Recovery menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: