Azure Logic Apps: 7 Powerful Ways to Automate Workflows Instantly
Imagine connecting your apps, services, and data without writing a single line of code. With Azure Logic Apps, that’s not just possible—it’s effortless. This cloud-based service empowers businesses to automate complex workflows across multiple platforms with stunning simplicity and scalability.
What Are Azure Logic Apps?
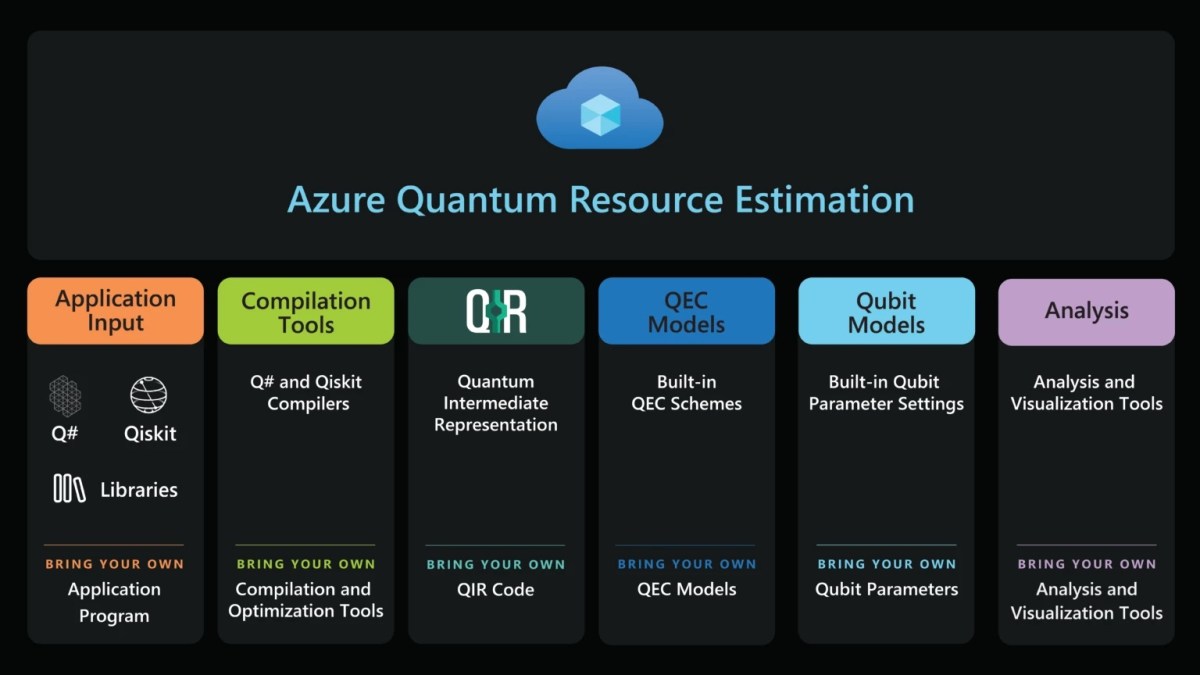
Azure Logic Apps is a fully managed, cloud-based service from Microsoft that enables you to design, build, and deploy scalable integrations and automated workflows. Whether you’re connecting SaaS applications like Salesforce or Office 365, or integrating on-premises systems via connectors, Logic Apps handles it all with a visual designer that makes automation accessible—even to non-developers.
Core Purpose and Vision
The primary goal of Azure Logic Apps is to simplify integration across disparate systems. In today’s digital landscape, organizations use dozens of applications—each operating in silos. Logic Apps bridges these gaps by enabling seamless data flow and process automation without requiring deep coding expertise.
- Automates business processes across cloud and on-premises systems
- Reduces dependency on custom-coded integrations
- Enables rapid deployment of workflows using a drag-and-drop interface
According to Microsoft’s official documentation, Logic Apps are designed for “low-code, high-impact” automation, making them ideal for both IT professionals and business analysts [Microsoft Learn].
How It Fits in the Azure Ecosystem
Azure Logic Apps doesn’t operate in isolation. It’s a key component of Microsoft’s broader integration platform, working alongside services like Azure Functions, API Management, and Event Grid. This interconnected architecture allows developers to build robust, event-driven solutions at scale.
“Azure Logic Apps enables organizations to connect apps, data, and services across enterprises and clouds to automate business processes and IT operations.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
Its tight integration with Azure Active Directory, Azure Monitor, and Azure DevOps ensures secure, monitored, and CI/CD-ready workflows, making it a cornerstone for enterprise-grade automation.
Key Features of Azure Logic Apps
Azure Logic Apps stands out due to its rich set of features that cater to both technical and non-technical users. From visual workflow design to enterprise-grade security, the platform offers everything needed to automate modern business processes efficiently.
Visual Workflow Designer
The Logic Apps Designer is a browser-based, drag-and-drop interface that allows users to create workflows by connecting triggers and actions. Each step in the workflow is represented as a card, making it easy to visualize the entire process flow.
- Real-time validation and error highlighting
- Pre-built templates for common scenarios (e.g., file processing, email notifications)
- Support for JSON-based definition editing for advanced users
This designer drastically reduces development time. For example, setting up an automated approval workflow between SharePoint and Outlook can be done in under 15 minutes—without writing any code.
Rich Connector Library
One of the most powerful aspects of Azure Logic Apps is its extensive library of over 300 built-in connectors. These connectors allow seamless integration with popular services such as:
- Microsoft 365 (formerly Office 365)
- Salesforce, Dynamics 365
- Dropbox, Google Drive, OneDrive
- Azure Storage, SQL Database, Service Bus
- SAP, Oracle, IBM MQ (via on-premises data gateway)
Connectors are categorized into cloud, enterprise, and partner types. Enterprise connectors often require licensing but provide deep integration capabilities for legacy systems. You can explore the full list of connectors on Microsoft’s Connectors Reference Page.
Built-in Triggers and Actions
Every workflow in Azure Logic Apps starts with a trigger—the event that initiates the process. Common triggers include:
- When a new email arrives (Outlook)
- When a file is added to a folder (OneDrive or SharePoint)
- Recurrence (scheduled intervals)
- HTTP request received (for API-style workflows)
After the trigger, you add actions—steps that perform specific tasks. Actions can include sending emails, updating databases, calling REST APIs, or invoking Azure Functions. The combination of triggers and actions forms the backbone of any automated workflow.
How Azure Logic Apps Work: The Architecture
Understanding the underlying architecture of Azure Logic Apps is crucial for designing efficient and scalable workflows. The service operates on a serverless model, meaning you don’t manage infrastructure—Microsoft does.
Workflow Execution Model
When a workflow is triggered, Azure Logic Apps spins up an instance to execute the defined steps. Each run is stateless by default, but the service automatically persists state between steps, allowing long-running workflows (even those lasting days or weeks) to resume correctly.
- Runs are billed per action execution and connector usage
- State persistence is handled via Azure Storage
- Concurrency control ensures scalability under load
This execution model makes Logic Apps highly scalable and cost-effective, especially for intermittent or event-driven processes.
Integration with Azure Services
Azure Logic Apps integrates tightly with several core Azure services to enhance functionality:
- Azure Functions: For custom code execution within a workflow
- Azure API Management: To expose Logic Apps as managed APIs
- Azure Event Grid: For event-driven architectures and real-time processing
- Azure Monitor: For logging, monitoring, and alerting
For example, you can use Event Grid to trigger a Logic App when a blob is uploaded to Azure Storage, then use Azure Functions to process the file content, and finally store the result in Cosmos DB—all orchestrated seamlessly.
Stateful vs. Stateless Workflows
Azure Logic Apps supports both stateless and stateful workflows:
- Stateless: Short-lived, high-throughput workflows (e.g., API endpoints). These are optimized for performance and low latency.
- Stateful: Long-running workflows that maintain context across days or weeks (e.g., approval processes with human interaction). These automatically save state after each step.
Choosing the right type depends on your use case. Stateful workflows are ideal for business processes involving delays or manual steps, while stateless ones suit real-time data processing.
Use Cases and Real-World Scenarios
Azure Logic Apps shines in real-world applications where automation can eliminate manual effort, reduce errors, and accelerate business operations. Let’s explore some common and impactful use cases.
Automating File Processing
Many organizations deal with repetitive file-handling tasks—like receiving invoices via email, extracting data, and uploading to a database. Azure Logic Apps can automate this entire pipeline.
- Trigger: New email with attachment in Outlook
- Action: Save attachment to Azure Blob Storage
- Action: Call Azure Function to parse PDF invoice
- Action: Insert data into SQL Database
- Action: Send confirmation email
This end-to-end automation reduces processing time from hours to seconds and minimizes human error.
Business Process Automation
Approval workflows are a classic example. Imagine an employee submits a leave request in SharePoint. A Logic App can:
- Trigger when a new item is added
- Send an approval request to the manager via Teams or email
- Wait for response (stateful workflow)
- Update the SharePoint list based on approval status
- Notify HR system via API
This kind of automation improves transparency, speeds up decisions, and integrates seamlessly with existing tools.
IT and DevOps Automation
Logic Apps isn’t just for business users—it’s also a powerful tool for IT teams. You can automate tasks like:
- Monitoring Azure resources and sending alerts via Slack or email
- Scaling VMs based on schedule or metrics
- Backing up databases and storing logs in a central location
- Triggering CI/CD pipelines in Azure DevOps upon code commit
By integrating with Azure Monitor and Event Grid, Logic Apps becomes a central nervous system for proactive IT operations.
Benefits of Using Azure Logic Apps
Organizations adopting Azure Logic Apps gain significant advantages in agility, cost, and operational efficiency. Let’s break down the key benefits.
Low-Code Development for Faster Delivery
One of the biggest advantages is the low-code nature of Logic Apps. Business analysts and power users can build workflows without relying on developers. This accelerates project delivery and reduces bottlenecks.
- Drag-and-drop interface lowers the learning curve
- Pre-built templates speed up development
- Collaboration between IT and business teams improves
According to a Forrester study, organizations using low-code platforms report up to 70% faster time-to-market for integration projects.
Scalability and Reliability
As a fully managed Azure service, Logic Apps automatically scales to handle workload spikes. Whether you’re processing 10 or 10,000 events per hour, the platform adjusts seamlessly.
- No infrastructure to manage
- High availability built-in (SLA of 99.9%)
- Automatic retries and error handling
This reliability is critical for mission-critical workflows like order processing or customer onboarding.
Cost-Effectiveness
Azure Logic Apps uses a consumption-based pricing model. You only pay for what you use—per action, connector, and execution duration.
- No upfront costs or long-term commitments
- Ideal for sporadic or event-driven workflows
- Transparent pricing with no hidden fees
Compared to building and maintaining custom integration solutions, Logic Apps can reduce total cost of ownership by up to 60%, according to Microsoft case studies.
Best Practices for Designing Logic Apps
To get the most out of Azure Logic Apps, it’s essential to follow best practices in design, security, and maintenance. These guidelines ensure your workflows are efficient, secure, and easy to manage.
Optimize Workflow Performance
Poorly designed workflows can lead to delays, timeouts, or excessive costs. To optimize performance:
- Minimize the number of actions—combine steps where possible
- Use asynchronous patterns for long-running tasks
- Leverage batching when processing multiple items
- Avoid unnecessary data transformations in the workflow
For example, instead of calling an API for each record in a loop, use the “Apply to each” action with batch processing enabled.
Secure Your Workflows
Security is paramount when integrating sensitive systems. Azure Logic Apps provides several layers of protection:
- Use Managed Identities to authenticate with Azure resources (no secrets stored)
- Enable HTTPS for all HTTP actions
- Apply role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict who can edit or run workflows
- Use Azure Key Vault to store credentials and connection strings
Never hardcode passwords or API keys in the workflow definition. Always use secure parameters or Key Vault references.
Monitor and Troubleshoot Effectively
Even the best-designed workflows can fail. Azure Monitor and Log Analytics provide deep visibility into workflow runs.
- Enable diagnostic settings to send logs to Log Analytics
- Set up alerts for failed runs or high latency
- Use the Run History view in the Azure portal to inspect individual executions
- Leverage Application Insights for advanced telemetry
Regular monitoring helps identify bottlenecks, errors, and usage patterns—enabling continuous improvement.
Advanced Capabilities: Beyond Basic Automation
While Azure Logic Apps excels at simple integrations, its advanced features unlock even greater potential for complex, enterprise-grade solutions.
Custom Connectors
If your organization uses a proprietary API or a service not in the built-in connector list, you can create a custom connector. This allows Logic Apps to interact with any RESTful API.
- Define the API schema using OpenAPI (Swagger)
- Configure authentication (OAuth, API key, etc.)
- Test and publish the connector for reuse across workflows
Custom connectors are versioned and can be shared across your Azure tenant, promoting consistency and reusability.
Integration with Azure Functions
Sometimes, you need to execute custom logic that can’t be handled by standard actions. Azure Functions—a serverless compute service—integrates seamlessly with Logic Apps.
- Call a Function from a Logic App action
- Pass data in JSON format
- Return results to continue the workflow
For example, you might use a Function to perform complex data validation, image processing, or machine learning inference before proceeding.
Enterprise Integration Pack (EIP)
For organizations with legacy systems, the Enterprise Integration Pack (available in Integration Service Environment) provides advanced B2B capabilities:
- AS2, X12, EDIFACT message support
- Schema validation and message transformation
- Agreement management for partner communications
This makes Azure Logic Apps a viable alternative to traditional ESBs (Enterprise Service Buses) for hybrid integration scenarios.
Getting Started with Azure Logic Apps
Ready to build your first workflow? Here’s a step-by-step guide to get started with Azure Logic Apps in minutes.
Create Your First Logic App
1. Sign in to the Azure Portal.
2. Click “Create a resource” and search for “Logic App.”
3. Select the Logic App service and click “Create.”
4. Fill in basic details: name, subscription, resource group, location.
5. Choose the hosting plan (Consumption or Standard).
6. Click “Review + create,” then “Create.”
Once deployed, open the Logic App and click “Logic App Designer” to start building.
Build a Simple Workflow
Let’s create a workflow that sends an email when a new file is added to OneDrive:
- Choose the trigger: “When a file is created” (OneDrive connector)
- Sign in to your OneDrive account
- Select the folder to monitor
- Add an action: “Send an email” (Outlook connector)
- Enter recipient, subject, and body (include dynamic content like file name)
- Save the workflow
Now, whenever you upload a file to the specified folder, an email will be sent automatically.
Deploy and Manage Workflows
For production use, adopt DevOps practices:
- Use Azure DevOps or GitHub Actions for CI/CD pipelines
- Store Logic App definitions (JSON) in version control
- Deploy using ARM templates or Bicep files
- Use different environments (dev, test, prod) with configuration overrides
This ensures consistency, traceability, and rollback capability across deployments.
What is Azure Logic Apps used for?
Azure Logic Apps is used to automate workflows and integrate apps, data, and services across cloud and on-premises environments. Common uses include file processing, approval workflows, IT automation, and B2B integrations.
Is Azure Logic Apps free to use?
Azure Logic Apps offers a free tier with limited executions, but most production workloads use the Consumption or Standard pricing model, where you pay per action and connector usage. Costs vary based on execution volume and features used.
How does Azure Logic Apps differ from Azure Functions?
Azure Logic Apps is a workflow orchestration tool focused on integration and automation using a visual designer, while Azure Functions is a serverless compute service for running small pieces of code. They are complementary and often used together.
Can Logic Apps connect to on-premises systems?
Yes, Logic Apps can connect to on-premises systems using the On-Premises Data Gateway, which securely bridges cloud workflows with local databases, file shares, and enterprise applications like SAP or SQL Server.
What is the difference between Consumption and Standard plans?
The Consumption plan is serverless, scales automatically, and charges per execution. The Standard plan runs on Azure App Service, supports long-running workflows, custom code, and offers more control over deployment and networking.
Azure Logic Apps transforms the way organizations automate processes. With its intuitive design, vast connector library, and deep Azure integration, it empowers teams to build powerful workflows without writing code. Whether you’re automating simple tasks or orchestrating complex enterprise integrations, Logic Apps delivers speed, reliability, and scalability. By following best practices and leveraging advanced features like custom connectors and Functions integration, you can unlock endless automation possibilities in the cloud.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: