Azure SQL Database: 7 Powerful Reasons to Choose It Now
If you’re looking for a reliable, scalable, and secure cloud database, Azure SQL Database is your ultimate solution. Backed by Microsoft’s robust cloud infrastructure, it offers enterprise-grade performance with minimal management overhead.
What Is Azure SQL Database?

Azure SQL Database is Microsoft’s fully managed relational database service built on the SQL Server engine, hosted in the Microsoft Azure cloud. It’s designed to help organizations run scalable, high-performance applications without the burden of managing physical infrastructure.
Core Architecture and Design
At its foundation, Azure SQL Database uses the same SQL Server database engine as on-premises SQL Server, ensuring compatibility with existing applications and tools. However, it’s optimized for the cloud with automated backups, built-in high availability, and intelligent performance tuning.
- Runs on the latest stable version of SQL Server Engine
- Supports T-SQL, stored procedures, views, and functions
- Automatically handles patching, updates, and health monitoring
This architecture allows developers and DBAs to focus on application logic rather than infrastructure maintenance. Microsoft manages the underlying hardware, virtualization, and operating system, freeing up IT teams for more strategic tasks.
Deployment Models: Single Database vs. Elastic Pool
Azure SQL Database offers two primary deployment models: Single Database and Elastic Pool. Each serves different use cases based on workload requirements and cost considerations.
- Single Database: Ideal for standalone applications with predictable workloads. Each database operates independently with dedicated resources.
- Elastic Pool: Perfect for managing multiple databases (e.g., SaaS applications) where workloads vary. Resources are shared across databases, optimizing cost and performance.
For example, a software-as-a-service (SaaS) provider managing hundreds of customer databases can use elastic pools to balance resource consumption during peak hours. This model reduces costs by avoiding over-provisioning for each individual database.
“Azure SQL Database enables developers to build applications faster by removing the complexity of database administration.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
Key Features of Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Database stands out due to its rich set of intelligent, automated, and secure features. These capabilities make it one of the most advanced cloud databases available today.
Intelligent Performance Optimization
One of the standout features of Azure SQL Database is its built-in intelligence. The service uses machine learning to continuously monitor and optimize query performance.
- Automatic tuning suggests and applies index optimizations
- Query Performance Insights helps identify slow-running queries
- Adaptive query processing improves execution plans dynamically
For instance, if a query suddenly starts performing poorly due to data growth, Azure SQL Database can detect this and recommend or automatically create missing indexes. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and boosts application responsiveness.
Advanced Security and Compliance
Security is a top priority in cloud environments, and Azure SQL Database delivers comprehensive protection at every level.
- Always Encrypted ensures sensitive data remains encrypted even during processing
- Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) protects data at rest
- Advanced Threat Protection detects anomalous activities and potential breaches
Additionally, Azure SQL Database complies with major regulatory standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and SOC 1/2. This makes it suitable for industries like healthcare, finance, and government that require strict data governance.
High Availability and Disaster Recovery
Downtime can be costly, which is why Azure SQL Database guarantees 99.99% availability for all service tiers.
- Built-in replication across multiple nodes within a region
- Zone-redundant configurations for protection against datacenter failures
- Active Geo-Replication allows up to four readable secondary databases in different regions
In the event of a regional outage, applications can fail over to a secondary region with minimal disruption. This capability is essential for global businesses requiring continuous operations.
Scalability and Performance Tiers
Azure SQL Database offers flexible scalability options that allow businesses to adjust resources based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Provisioned Compute vs. Serverless
There are two main compute models: Provisioned and Serverless.
- Provisioned Compute: You reserve a specific amount of compute power (measured in DTUs or vCores). Best for consistent, predictable workloads.
- Serverless: Automatically scales compute based on workload activity. Ideal for intermittent or unpredictable usage patterns.
The serverless option is particularly beneficial for development environments, testing, or applications with variable traffic. It starts up quickly when needed and pauses during inactivity, reducing costs significantly.
DTU vs. vCore Purchasing Models
Understanding the difference between DTU and vCore models is crucial for effective resource planning.
- DTU Model: Bundles CPU, memory, and I/O into a single metric. Simpler for beginners but less granular control.
- vCore Model: Allows independent selection of CPU, memory, and storage. Offers greater flexibility and transparency, especially for enterprise workloads.
For example, a large enterprise migrating from on-premises SQL Server might prefer the vCore model because it allows them to match their existing hardware specs more precisely. Meanwhile, a startup might opt for the DTU model for simplicity.
Integration with Azure Ecosystem
Azure SQL Database doesn’t exist in isolation—it’s deeply integrated with the broader Azure platform, enabling seamless workflows and enhanced functionality.
Seamless Connectivity with Azure Services
Azure SQL Database works effortlessly with other Azure services such as Azure App Service, Azure Functions, Logic Apps, and Power BI.
- Direct connection to Azure Web Apps for backend data storage
- Integration with Azure Data Factory for ETL pipelines
- Real-time analytics using Power BI dashboards connected directly to the database
This tight integration reduces development time and simplifies deployment. For example, a marketing team can use Power BI to visualize customer data stored in Azure SQL Database without needing complex middleware.
Hybrid Scenarios with Azure Arc
For organizations with hybrid cloud strategies, Azure Arc enables management of SQL databases across on-premises, edge, and multi-cloud environments from a single control plane.
- Extend Azure management to SQL Server instances outside Azure
- Apply consistent policies, security, and monitoring across environments
- Gradual migration path from on-premises to cloud
This is especially valuable for enterprises undergoing digital transformation but not ready to fully move to the cloud. Azure Arc provides a unified experience while maintaining flexibility.
Migrating to Azure SQL Database
Migrating existing databases to the cloud can seem daunting, but Azure provides tools and guidance to streamline the process.
Assessment and Readiness Check
Before migration, it’s essential to assess database compatibility and performance requirements.
- Use the Azure Database Migration Guide to evaluate readiness
- Leverage Data Migration Assistant (DMA) to identify compatibility issues
- Analyze workload patterns to choose the right service tier
DMA scans your on-premises SQL Server instance and provides recommendations for schema changes, deprecated features, and performance improvements before migration.
Migration Tools and Strategies
Azure offers several tools to facilitate smooth migration:
- Azure Database Migration Service (DMS): Performs online migrations with minimal downtime
- Backup and Restore: Restore .bak files directly to Azure SQL Database Managed Instance
- Transactional Replication: Keep source and target synchronized during migration
For example, a financial institution can use DMS to migrate a 5 TB database over a weekend with only minutes of downtime, ensuring business continuity.
Monitoring and Management
Effective monitoring is critical to maintaining performance, security, and cost control in any cloud environment.
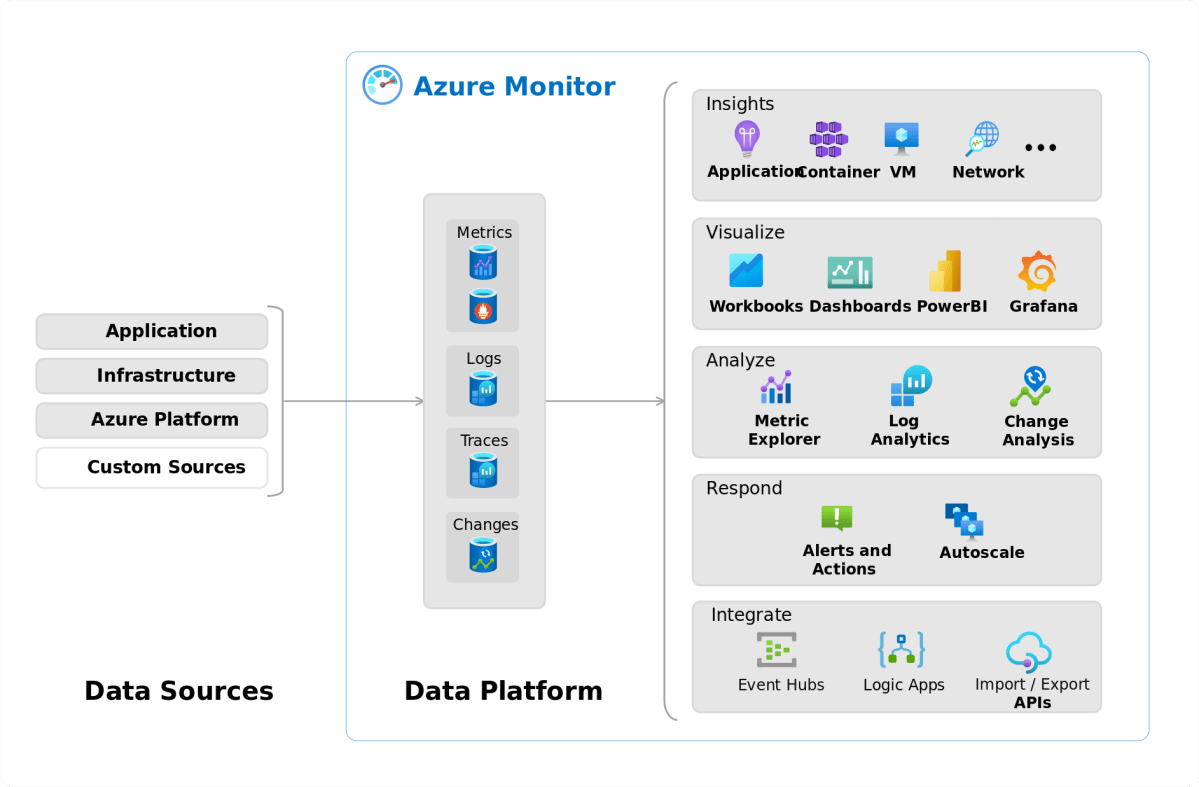
Using Azure Monitor and Metrics
Azure Monitor provides comprehensive insights into database performance and health.
- Track CPU usage, memory consumption, and DTU percentage
- Set up alerts for threshold breaches
- Visualize metrics using dashboards
You can configure alerts to notify your DevOps team when CPU usage exceeds 80% for more than 5 minutes, allowing proactive intervention before performance degrades.
Query Performance Insights
Query Performance Insights is a powerful tool within the Azure portal that helps identify the most resource-intensive queries.
- View top CPU-consuming queries
- Analyze execution frequency and duration
- Drill down into query plans for optimization
By identifying inefficient queries early, teams can rewrite or index them to improve overall application performance.
Cost Management and Pricing
Understanding pricing models is essential to avoid unexpected bills and optimize spending.
Factors Affecting Azure SQL Database Costs
Several factors influence the total cost of running Azure SQL Database:
- Compute tier (Basic, Standard, Premium, Business Critical)
- Storage size and type (HDD vs. SSD)
- Data transfer and backup retention
- Number of databases in elastic pools
For example, a Premium-tier database with 1 TB of storage and geo-replication will cost significantly more than a Basic-tier database with 5 GB of storage. However, the performance and availability benefits may justify the expense for mission-critical applications.
Using the Azure Pricing Calculator
To estimate costs accurately, use the Azure Pricing Calculator.
- Select your preferred region
- Choose compute model (DTU or vCore)
- Adjust storage and backup settings
- Compare different tiers side by side
This tool helps you make informed decisions before deployment, ensuring alignment with budget constraints.
Best Practices for Azure SQL Database
Following best practices ensures optimal performance, security, and cost-efficiency.
Implement Proper Indexing and Statistics
Well-designed indexes are crucial for query performance.
- Regularly update statistics to help the query optimizer make better decisions
- Avoid over-indexing, which can slow down write operations
- Use filtered indexes for large tables with specific query patterns
For example, a retail application querying orders by date range can benefit from a filtered index on the order date column.
Leverage Automated Backups and Point-in-Time Restore
Azure SQL Database automatically creates full, differential, and transaction log backups.
- Backups are retained for 7 to 35 days depending on the service tier
- Point-in-time restore allows recovery to any second within the retention period
- Geo-restore enables recovery from a different region in case of regional failure
This eliminates the need for manual backup scripts and ensures data durability.
Secure Access with Firewall Rules and Authentication
Controlling access is vital to prevent unauthorized entry.
- Configure IP firewall rules to allow only trusted networks
- Use Azure Active Directory (AAD) authentication instead of SQL logins
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for admin accounts
Using AAD integration simplifies user management and enhances security through centralized identity control.
What is Azure SQL Database used for?
Azure SQL Database is used to host relational data for web, mobile, and enterprise applications in the cloud. It supports transactional processing, real-time analytics, and hybrid scenarios, making it ideal for SaaS platforms, e-commerce sites, and line-of-business applications.
How does Azure SQL Database differ from SQL Server on-premises?
While both use the same SQL engine, Azure SQL Database is a fully managed service with automatic updates, backups, and scaling. On-premises SQL Server requires manual administration, hardware maintenance, and licensing management.
Is Azure SQL Database secure?
Yes, Azure SQL Database includes multiple layers of security such as encryption (at rest and in transit), threat detection, firewall rules, and integration with Azure Active Directory for identity management.
Can I migrate my existing SQL Server database to Azure SQL Database?
Yes, you can migrate using tools like Data Migration Assistant and Azure Database Migration Service. These tools help assess compatibility, transfer schema and data, and minimize downtime during migration.
What is the difference between Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance?
Azure SQL Database is best for cloud-native applications needing scalability and low management overhead. Azure SQL Managed Instance offers near 100% compatibility with on-premises SQL Server, making it ideal for lift-and-shift migrations with minimal code changes.
In conclusion, Azure SQL Database is a powerful, intelligent, and secure cloud database platform that empowers organizations to innovate faster and operate more efficiently. With its automated management, elastic scalability, deep integration with Azure services, and robust security features, it’s an ideal choice for modern application development. Whether you’re building a new cloud-native app or migrating legacy systems, Azure SQL Database provides the tools and reliability needed to succeed in today’s digital landscape.
Further Reading: