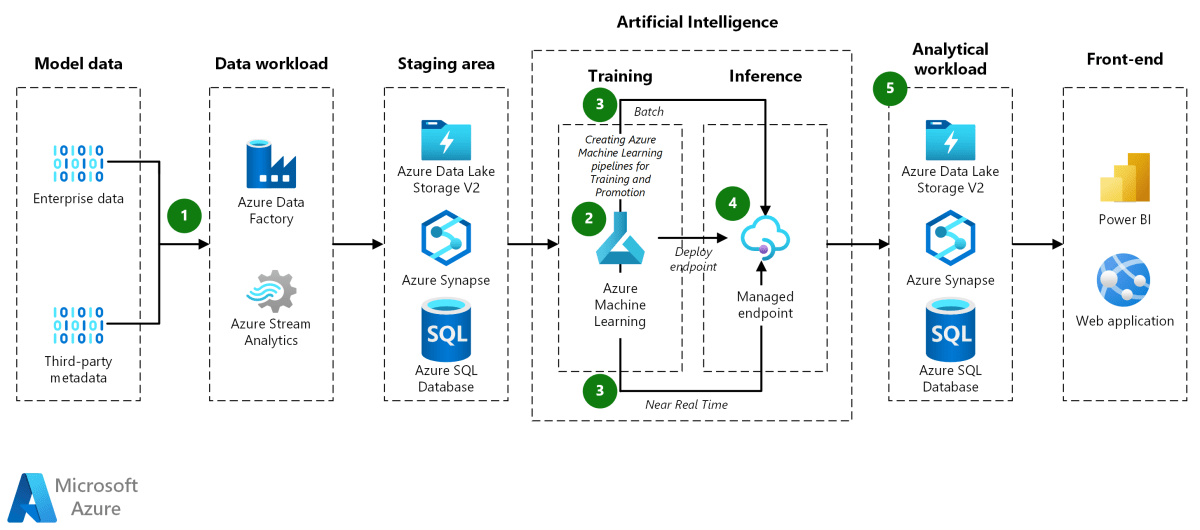
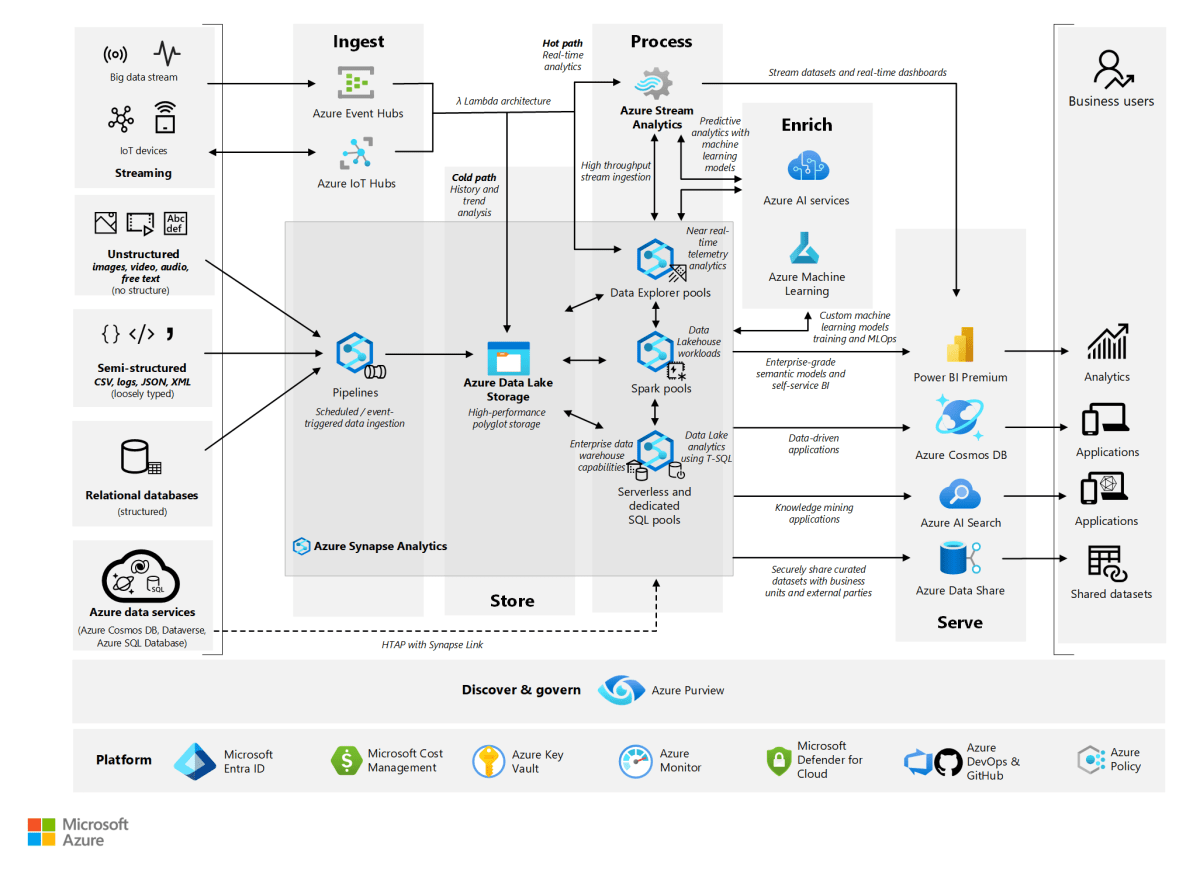
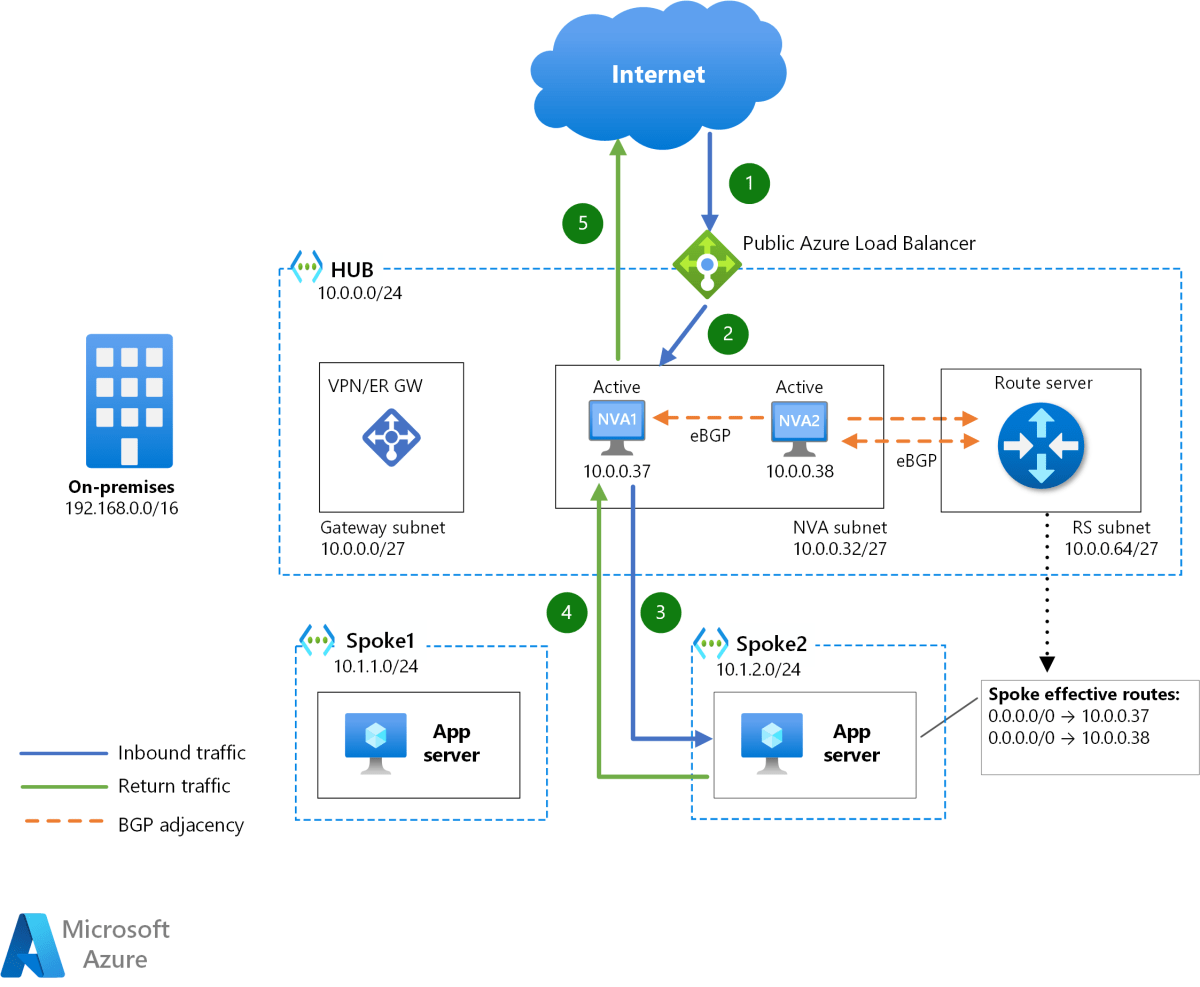
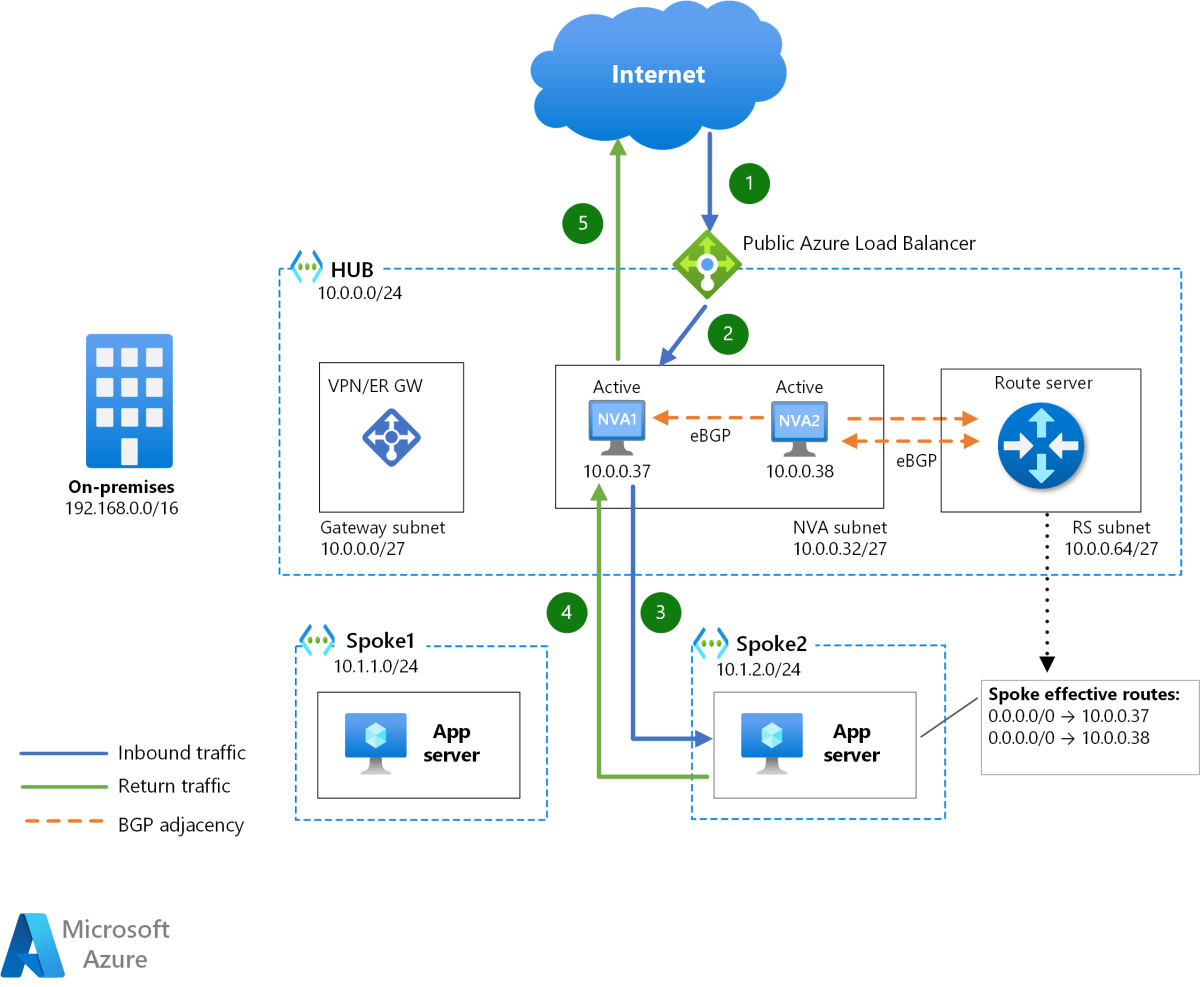
Azure Virtual Network : 7 Powerful Insights You Must Know
Welcome to the world of cloud networking! If you’re diving into Microsoft Azure, understanding Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is your first critical step. Think of it as the backbone of your cloud infrastructure—secure, scalable, and fully customizable.
What Is Azure Virtual Network (VNet)?

The Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is the fundamental building block for private networks in Microsoft Azure. It enables Azure resources to securely communicate with each other, the internet, and on-premises networks. Essentially, a VNet is your own slice of the Azure cloud—a logically isolated section where you can launch Azure resources like virtual machines (VMs), app services, and more.
Core Definition and Purpose
An Azure Virtual Network (VNet) allows you to define your own IP address space using CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) blocks. You can segment this space into subnets, apply network security policies, and control traffic flow. This level of control mimics traditional on-premises networks but with the flexibility and scalability of the cloud.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Azure Virtual Network (VNet) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Provides isolation and segmentation within the Azure cloud.
- Enables private IP addressing and DNS configuration.
- Supports both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols.
How VNet Differs from Traditional Networking
Unlike physical networks that rely on routers, switches, and cabling, Azure Virtual Network (VNet) operates in a software-defined environment. This means all network logic—routing, filtering, load balancing—is handled virtually, giving you greater agility and automation capabilities.
- No physical hardware to manage.
- Instant provisioning and configuration via APIs or the Azure portal.
- Dynamic scaling based on workload demands.
“Azure Virtual Network is the foundation of Azure networking. Everything connects through it—your VMs, your applications, your hybrid connections.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) Architecture and Components
To fully leverage the power of Azure Virtual Network (VNet), you need to understand its core architectural components. These elements work together to provide a secure, high-performance network environment in the cloud.
Subnets: The Building Blocks of VNet
Subnets divide a VNet into smaller IP address ranges, allowing for better organization and security. Each subnet can host different types of resources and have distinct access controls applied via Network Security Groups (NSGs).
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Azure Virtual Network (VNet) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Recommended to separate tiers (e.g., web, app, database) into different subnets.
- Supports service delegation (e.g., assigning a subnet to Azure Kubernetes Service).
- Can be protected with NSGs and route tables.
Network Security Groups (NSGs)
NSGs act as virtual firewalls that control inbound and outbound traffic to subnets or individual network interfaces. They use rules based on source/destination IP, port, and protocol to allow or deny traffic.
- Can be associated with subnets or NICs.
- Support both default and custom rules.
- Integrate with Azure Firewall and Web Application Firewall (WAF) for advanced protection.
Route Tables and User-Defined Routing
By default, Azure handles routing within VNets automatically. However, you can override this behavior using custom route tables. This is useful when directing traffic through virtual appliances or enforcing specific network paths.
- Support up to 400 routes per route table.
- Can be linked to multiple subnets.
- Enable scenarios like forced tunneling to on-premises networks.
Key Benefits of Using Azure Virtual Network (VNet)
Deploying an Azure Virtual Network (VNet) offers numerous advantages for organizations moving to the cloud. From enhanced security to seamless integration, VNets are essential for any serious Azure deployment.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Azure Virtual Network (VNet) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Enhanced Security and Isolation
One of the biggest advantages of Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is the ability to isolate your resources from the public internet and other tenants in the cloud. With private IP addressing and NSGs, you can create a zero-trust environment where only authorized traffic is allowed.
- Resources in a VNet are not publicly accessible by default.
- Micro-segmentation reduces the attack surface.
- Integration with Azure Policy ensures compliance at scale.
Scalability and Flexibility
As your business grows, so can your VNet. You can expand IP ranges, add new subnets, and connect to other VNets or on-premises networks without downtime. This elasticity is crucial for handling unpredictable workloads.
- Supports up to 100 VNets per region per subscription (can be increased).
- Allows overlapping IP addresses across peered VNets with proper planning.
- Integrates with Azure Virtual WAN for global scale networking.
Seamless Hybrid Connectivity
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) excels at connecting cloud and on-premises environments. Whether you’re using Site-to-Site VPN, ExpressRoute, or Point-to-Site connections, VNets serve as the endpoint for secure hybrid networking.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Azure Virtual Network (VNet) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- ExpressRoute offers private, high-speed connections with SLA-backed uptime.
- Site-to-Site VPN uses IPsec/IKE for encrypted tunnels over the internet.
- Point-to-Site is ideal for remote workers connecting securely to Azure resources.
Networking Scenarios with Azure Virtual Network (VNet)
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) supports a wide range of deployment scenarios, from simple single-tier applications to complex multi-region architectures. Understanding these use cases helps you design the right network topology for your needs.
Single VNet with Multiple Subnets
This is the most common scenario for small to medium applications. A single VNet contains multiple subnets (e.g., frontend, backend, database), each with appropriate NSG rules.
- Ideal for web applications with clear tier separation.
- Easy to manage and monitor.
- Can be extended later with VNet peering or gateways.
VNet Peering for Resource Sharing
VNet peering allows two VNets to communicate as if they were on the same network. Traffic flows through Microsoft’s backbone without going over the public internet, ensuring low latency and high security.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Azure Virtual Network (VNet) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Supports both regional and global peering.
- Enables cross-subscription and cross-tenant connectivity.
- Does not require gateways or public IPs for communication.
Learn more about VNet peering capabilities at Microsoft’s official documentation.
Hub-and-Spoke Topology
In enterprise environments, the hub-and-spoke model is widely used. The hub VNet acts as a central point for shared services (like firewalls, DNS, and gateways), while spoke VNets host application workloads.
- Improves security by centralizing traffic inspection.
- Reduces costs by sharing expensive resources like ExpressRoute gateways.
- Supports transitive routing when combined with virtual appliances.
Security and Compliance in Azure Virtual Network (VNet)
Security is not an afterthought in Azure—it’s built into the fabric of the platform. Azure Virtual Network (VNet) provides multiple layers of protection to keep your data safe and compliant with industry standards.
Network Security Groups vs. Azure Firewall
While NSGs provide basic layer 3 and 4 filtering, Azure Firewall offers stateful, fully managed firewall-as-a-service with advanced features like FQDN filtering, threat intelligence, and intrusion detection.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Azure Virtual Network (VNet) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- NSGs are free and ideal for simple allow/deny rules.
- Azure Firewall supports application-level filtering and logging.
- Can be deployed in a dedicated subnet within the VNet.
DDoS Protection Standard
Azure offers DDoS Protection plans to safeguard your public-facing resources. The Standard tier provides real-time monitoring, adaptive tuning, and attack mitigation.
- Automatically enabled for public IPs associated with VNet resources.
- Reduces downtime during volumetric attacks.
- Integrates with Azure Monitor for detailed reporting.
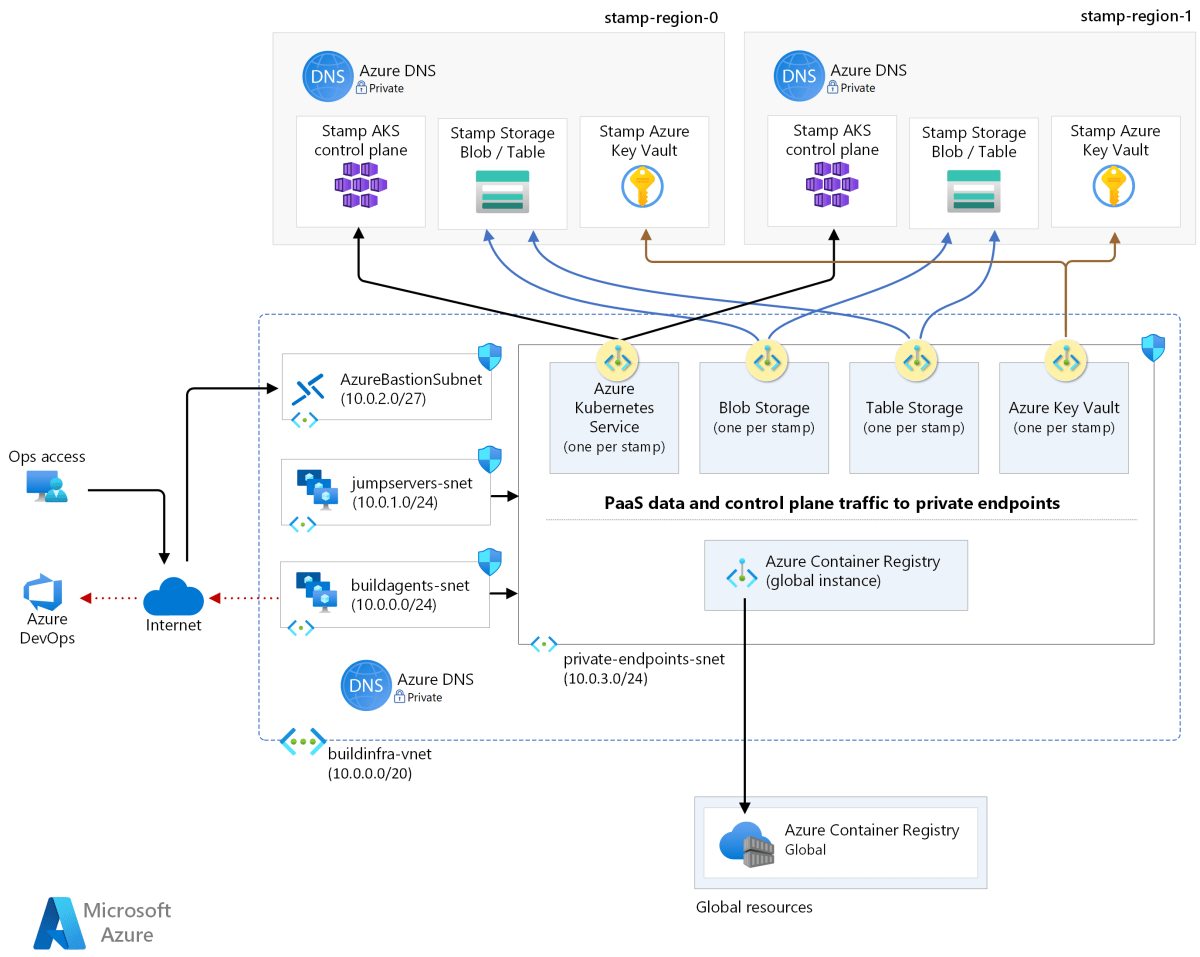
Private Link and Private Endpoints
To prevent data exfiltration and reduce exposure to the internet, Azure Private Link allows you to access PaaS services (like Azure Storage or SQL Database) over a private endpoint within your VNet.
- Eliminates the need for public IPs or NAT devices.
- Ensures traffic stays within the Microsoft backbone.
- Supports private DNS zones for seamless name resolution.
Explore how Private Endpoints enhance security at Azure Private Link Overview.
Hybrid Connectivity Options with Azure Virtual Network (VNet)
For organizations with existing on-premises infrastructure, Azure Virtual Network (VNet) provides robust hybrid connectivity options that ensure seamless integration between environments.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Azure Virtual Network (VNet) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Site-to-Site (S2S) VPN
A Site-to-Site VPN connects your on-premises network to an Azure VNet using an IPsec/IKE encrypted tunnel over the internet. It’s cost-effective and easy to set up.
- Requires a compatible on-premises VPN device.
- Supports up to 30 tunnels per gateway (depending on SKU).
- Ideal for development, testing, or non-latency-sensitive workloads.
ExpressRoute for Private Connectivity
ExpressRoute provides a private, high-bandwidth connection from your on-premises network to Azure via a connectivity provider. It bypasses the public internet entirely, offering higher reliability, faster speeds, and lower latencies.
- Available in bandwidths from 50 Mbps to 10 Gbps.
- Supports SLA-backed uptime (99.9% or 99.95%).
- Enables access to Microsoft 365 and Dynamics 365 services.
Point-to-Site (P2S) VPN
Point-to-Site VPN allows individual devices (like laptops) to connect securely to an Azure VNet. It’s perfect for remote workers or administrators who need secure access to cloud resources.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Azure Virtual Network (VNet) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Uses SSTP, IKEv2, or OpenVPN protocols.
- No need for a public-facing VPN device.
- Can be combined with Azure AD authentication for identity-based access.
Best Practices for Managing Azure Virtual Network (VNet)
Proper planning and management are key to maximizing the benefits of Azure Virtual Network (VNet). Following best practices ensures performance, security, and scalability over time.
Plan IP Addressing Carefully
Before creating a VNet, plan your IP address space to avoid conflicts, especially in hybrid scenarios. Use non-overlapping CIDR blocks and reserve space for future growth.
- Avoid using 10.0.0.0/8 if possible, as it’s commonly used on-premises.
- Use tools like Azure IP Address Manager (if available) or spreadsheets to track allocations.
- Consider using Azure Virtual Network Manager for centralized control.
Implement Network Segmentation
Segment your network into subnets based on function, sensitivity, or environment (dev, test, prod). Apply NSGs and route tables to enforce least-privilege access.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Azure Virtual Network (VNet) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Place public-facing resources in DMZ-like subnets.
- Restrict database access to application subnets only.
- Use service endpoints or private endpoints to secure PaaS access.
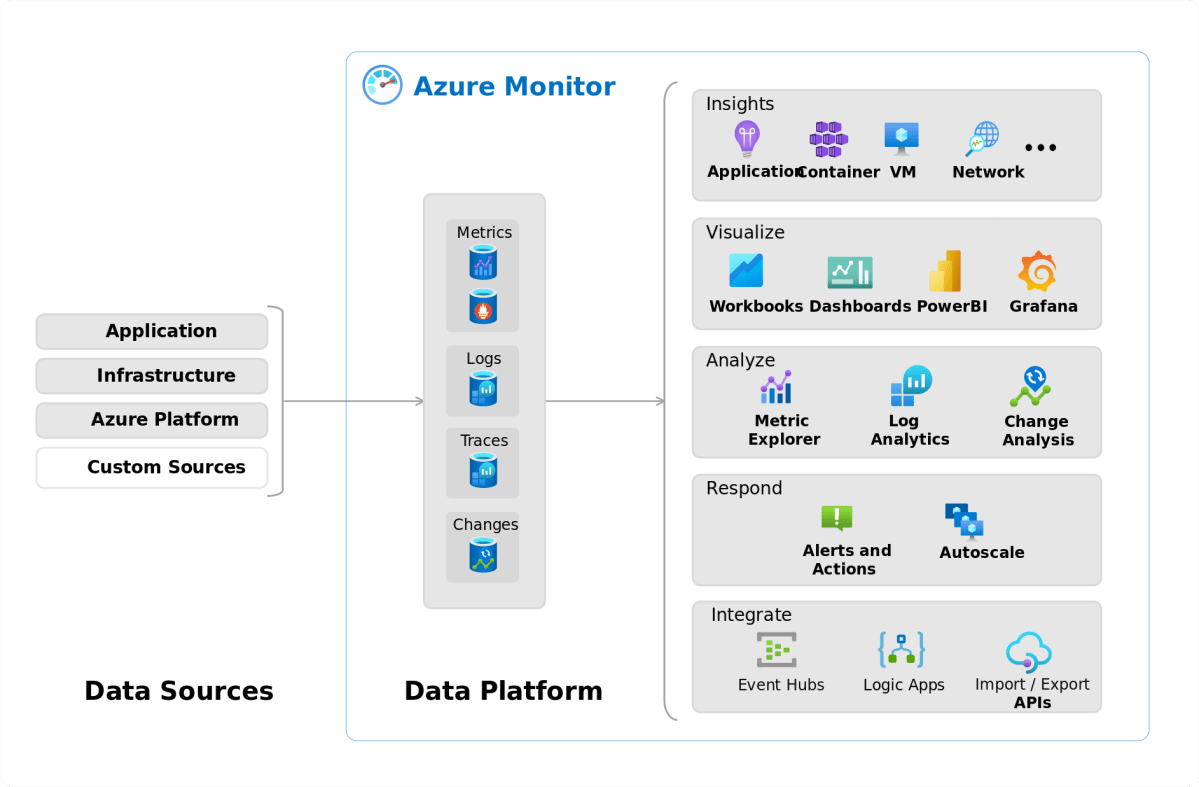
Monitor and Audit Network Traffic
Use Azure Monitor, Network Watcher, and Flow Logs to gain visibility into traffic patterns, detect anomalies, and troubleshoot issues.
- Enable VNet Flow Logs to capture allowed and denied traffic.
- Use Connection Monitor to test end-to-end connectivity.
- Set up alerts for unusual traffic spikes or security events.
Microsoft recommends enabling Azure Network Watcher in every region where you have VNets. Learn more at Azure Network Watcher Documentation.
Advanced Features and Integrations of Azure Virtual Network (VNet)
Beyond basic connectivity, Azure Virtual Network (VNet) integrates with a wide array of services to deliver advanced networking capabilities. These features empower enterprises to build resilient, high-performance cloud architectures.
Integration with Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
When deploying containerized applications using AKS, you can integrate the cluster directly into a VNet. This provides better network performance, security, and control over IP allocation.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Azure Virtual Network (VNet) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Enables static IP addresses for pods and services.
- Supports network policies for pod-to-pod communication.
- Allows AKS to access resources in other subnets or VNets via peering.
Virtual Network Tiers and Performance
Azure offers different performance levels based on VM size and network interface configuration. Understanding these tiers helps you optimize cost and performance.
- Basic tier: Limited bandwidth and features.
- Standard tier: Supports accelerated networking and larger throughput.
- Premium tier: For high-performance workloads like HPC or real-time analytics.
Azure Virtual WAN for Global Networking
Azure Virtual WAN is a networking service that brings together various network functionalities (branch connectivity, SD-WAN, routing, monitoring) into a single, optimized architecture. It integrates seamlessly with Azure Virtual Network (VNet).
- Automatically connects branches to Azure via IPsec tunnels.
- Provides a hub-spoke model with built-in gateways.
- Offers a centralized dashboard for global network management.
Discover how Azure Virtual WAN simplifies global networking at Azure Virtual WAN Overview.
What is Azure Virtual Network (VNet)?
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Azure Virtual Network (VNet) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is a service that provides isolated and private networking environments in Microsoft Azure. It allows Azure resources to securely communicate with each other, the internet, and on-premises networks using custom-defined IP address ranges, subnets, and security policies.
How does VNet peering work?
VNet peering connects two Azure Virtual Networks, enabling resources in both VNets to communicate over the Azure backbone network. It supports low-latency, high-bandwidth connectivity without requiring gateways or public internet exposure. Peering can be regional or global and allows cross-subscription and cross-tenant connections.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Azure Virtual Network (VNet) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Can I connect my on-premises network to Azure VNet?
Yes, you can connect your on-premises network to Azure Virtual Network (VNet) using Site-to-Site VPN, ExpressRoute, or Point-to-Site VPN. Site-to-Site and ExpressRoute are ideal for permanent connections, while Point-to-Site is suitable for remote users. ExpressRoute offers private, high-speed connectivity with SLA guarantees.
What is the difference between NSG and Azure Firewall?
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Azure Virtual Network (VNet) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Network Security Groups (NSGs) provide basic layer 3 and 4 filtering for inbound and outbound traffic to subnets or network interfaces. Azure Firewall is a fully managed, stateful firewall service that offers advanced features like FQDN filtering, threat intelligence, intrusion detection, and application-level filtering. It’s ideal for centralized security in hub-and-spoke architectures.
How do I secure PaaS services within a VNet?
You can secure access to Azure PaaS services (like Azure Storage or SQL Database) using Private Endpoints. This allows you to expose the service on a private IP address within your VNet, ensuring traffic stays within the Microsoft backbone and doesn’t traverse the public internet.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Azure Virtual Network (VNet) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Understanding Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is essential for anyone building cloud solutions on Microsoft Azure. From providing secure, isolated environments to enabling hybrid connectivity and advanced networking topologies, VNets form the foundation of modern cloud infrastructure. By leveraging features like subnets, NSGs, peering, and private endpoints, you can design scalable, secure, and high-performance networks. Whether you’re a developer, network engineer, or cloud architect, mastering Azure Virtual Network (VNet) empowers you to unlock the full potential of the Azure cloud.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Azure Virtual Network (VNet) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: